| Wan Chen K GRAHAM PhD (Agency for Integrated Care) and Chek Hooi WONG MBBS MPH (Geriatric Education & Research Institute) |
Key points:
Nursing home residents make up 0.04% of all COVID-19 cases in Singapore.
• As the total number of COVID-19 related deaths (n=27) is remarkably low, nursing home residents make up 11% of this figure even though there have only been 3 deaths to date.
• Key objectives of pandemic management in residential care are:
- To reduce the likelihood of COVID-19 entering nursing homes by restricting visits, increasing staff health surveillance, restricting movements of health care workers between facilities, and adhering to strict protocols for inter-facility transfers of residents.
- To reduce the impact of an infection if and when COVID-19 does enter a residential care facility. This is achieved through the creation of self-contained operational bubbles or split zones in care facilities and staff quarters; and through the close monitoring and early testing of residents with acute respiratory infections.
- To support the recovery of nursing homes after one or more residents have been found to be COVID-19 positive. This begins with swift testing of residents and staff in the affected zones within 24 hours to establish the extent of spread. Suspect and positive cases are transferred out for isolation and care in acute hospitals. Infection Prevention and Control principles are reinforced and the supply and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) is stepped up. Where necessary, manpower support drawn from other institutions is provided to ensure service continuity. Throughout all this, acute hospital partners are available to support the testing and medical management of residents and staff of affected nursing homes.
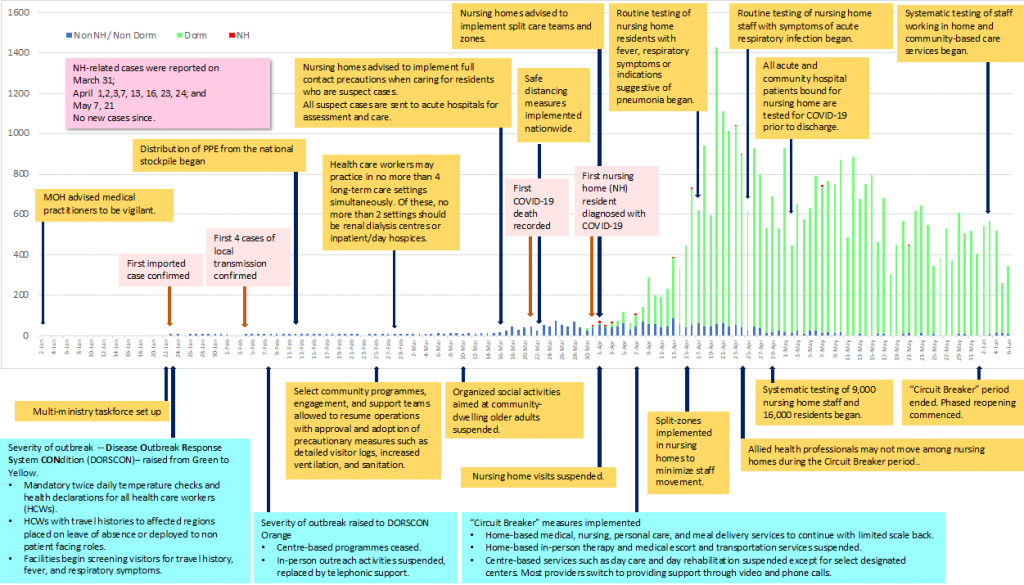
Figure: Long-term care related responses to COVID-19 in Singapore, January 2 to June 6, 2020